Counterbalanced Image Stabilizer
Counter-Balanced Image Stabilizer
This camera-shake compensating mechanism works passively and requires no electrical power, gyros or warm-up time. Developed by Steve Hines in 1977. Ref: Hines’ notebook p. 72. U.S. Pat. 4,290,684.
|
|
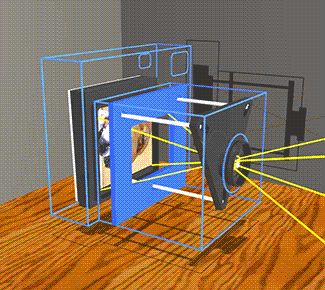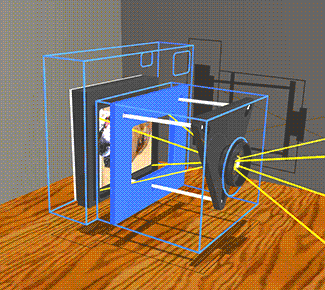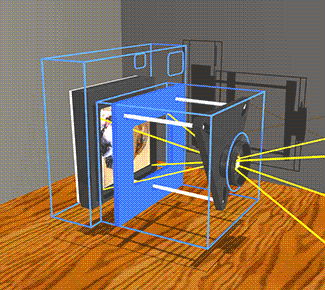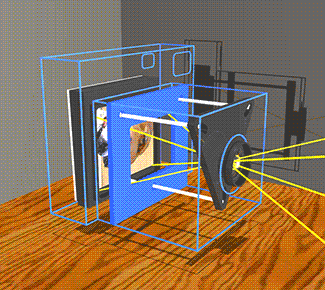
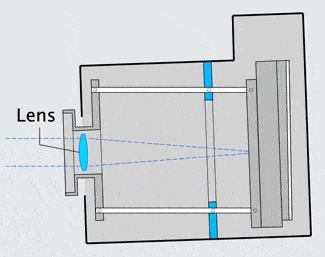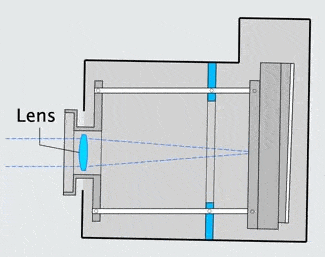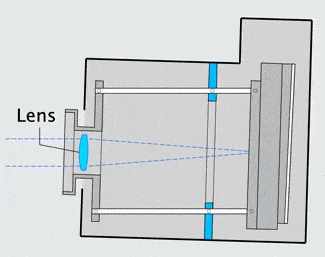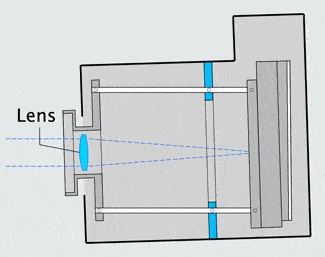
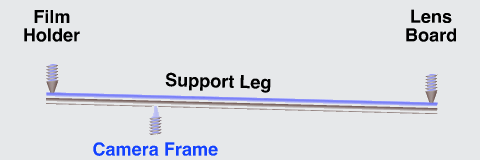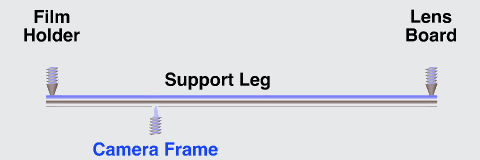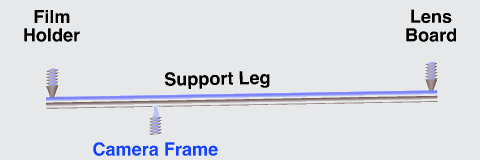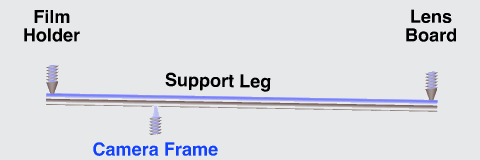
The image stabilizer in a clear camera body, showing the lens, film and holder, and three parallel support rods. The lens and film counter balance each other on opposite ends of the three rods which are the same length as the focal length of the camera lens, so as to not over or under correct image smear.
|
|
When the the camera shakes, inertia causes the mechanism to lag behind at the previous angle. The lens remains on a line between the object and its image on the film. |
|
Defocusing, based on a 100mm focal-length camera lens and support rods.
| Pitch or yaw |
mm, conventional mechanism (smaller is better) |
mm, this mechanism (smaller is better) |
| 0° | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1° | 1.15 | 0.02 |
| 2° | 2.3 | 0.06 |
| 3° | 3.46 | 0.14 |
| 4° | 4.62 | 0.22 |
| 5° | 5.9 | 0.38 |
What it provides:
Pitch and yaw camera motions have the most serious effect on image smear. Tipping a camera down 1°, has the effect of lifting an object 10 inches at a 50-foot distance. This shake-mechanism compensates for five times that amount of image smear..
This mechanism can withstand, but is not affected by, straight-line motion (being bumped).
The mechanism connects the rods to the lens board and film holder with agile cone-and-cup supports (the 3-D version of a knife-edge hinge).
The mechanism is released when taking the picture, but caged otherwise, for shipping, etc.
The concept applied to a 110-format camera:
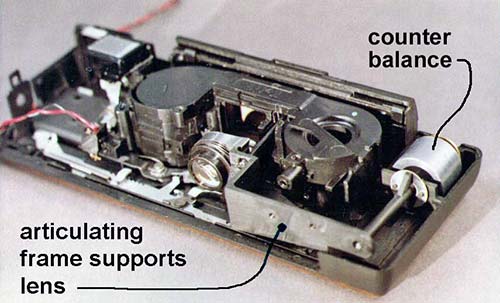
The weight of the lens is counterbalanced by the offset weight.
Steve Hines offers consulting in the area of opto-mechanical equipment design, and a variety of licensable technologies.
USA
email: [email protected]
ph.: 818-507-5812